Overview
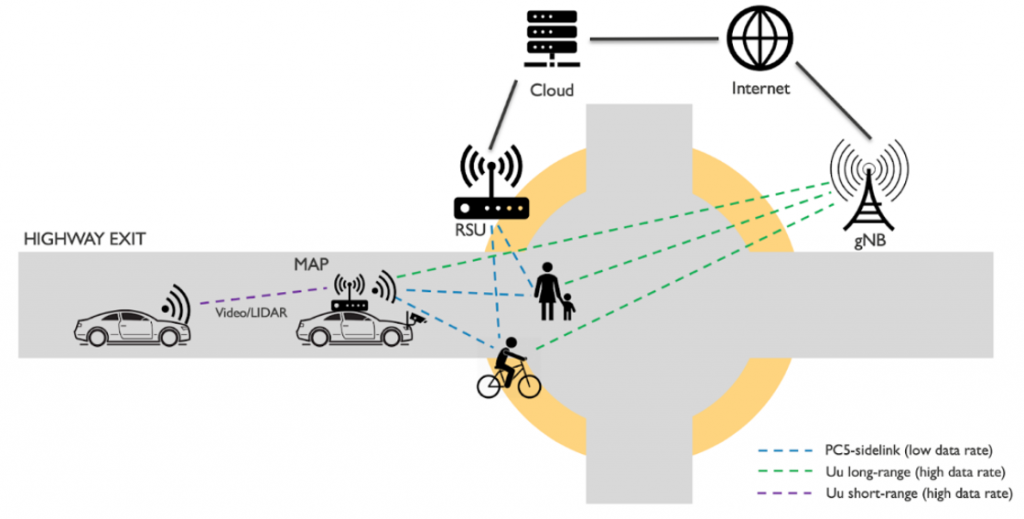
Smart Highway use case is executed in the context of smart mobility. The goal of this use case is to research and experiment beyond-5G connectivity to enhance safety on the road. Communications between vehicles and Vulnerable Road Users (VRUs) are expected to have small delays and to be highly reliable. Cars and roadside infrastructures are used as edges that provide services closer to the end users as well as to load-balance the computational resources. Furthermore, this use case demonstrates the coverage extension to ensure that the connectivity is always covered in the area by having a car that is mobile being exploited as a Mobile Access Point (MAP).
Use case stories
The two stories planned for the Smart Highway use case take place in two locations: Belgium for Story 1 and Germany for Story 2.
Story 1 – VRU Detection at the highway exit: The story emphasised on the point of view of the driver of a car that is about to enter an intersection from the highway exit. The intersection is used by cars, as well as VRUs. All road users should be aware of each other so that navigational decision can be taken more carefully as well as to avoid any sorts of accident. The car that is exiting the highway can detect the presence of the VRUs by obtaining the information from the existing cars on the intersection that also forwards the information towards the roadside infrastructures, or the Road Side Units (RSUs). The car that is already in the area can capture the presence of the VRUs from LiDAR or camera. At the same time, the VRUs also send a beacon to all road users about their presence. In this sense, the overall vision about the scenario and any harmful situation is amplified, bypassing any obstacle (e.g., bridges, buildings, or trees) in the way.
Story 2 – Distributed situation knowledge in shared traffic spaces: This story focuses on the efficiently distributed situational awareness and knowledge through the exchange of (processed and/or raw) sensor information between vehicles and RSUs and VRUs to increase road safety and improve traffic flow in shared traffic spaces. In shared traffic spaces, VRUs are recognized through the vehicle’s installed sensors (camera, LiDAR, etc.), the camera sensors are mounted on the RSU and the pedestrian’s smart device app, and this information is shared with the vehicle and the RSU, which act as a Mobile Access Point (MAP). Then, the Local Dynamic Map (LDM) is defined based on the shared information. While analysing the VRU’s movement and trajectory in real time on the LDM, it is possible to predict dangerous situations in shared traffic spaces and display warning messages on the vehicle’s screen and the VRUs’ app in real time to increase road safety.
Human centric applications
Story 1: VRU Detection at the highway exit
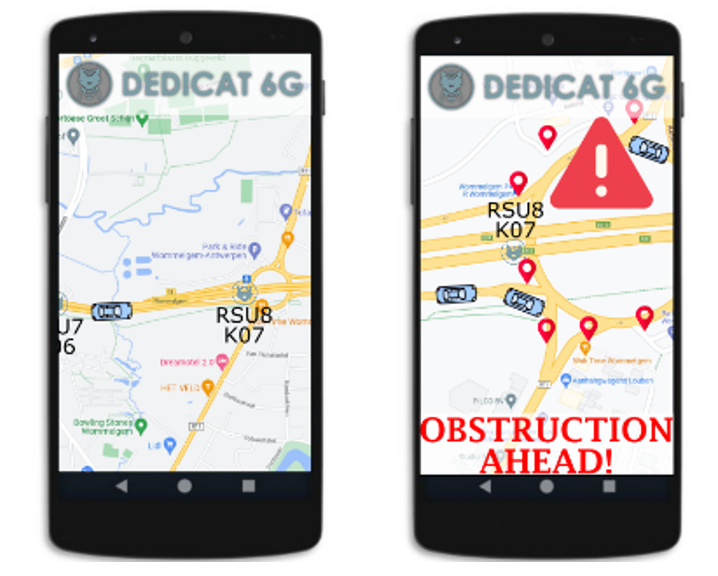
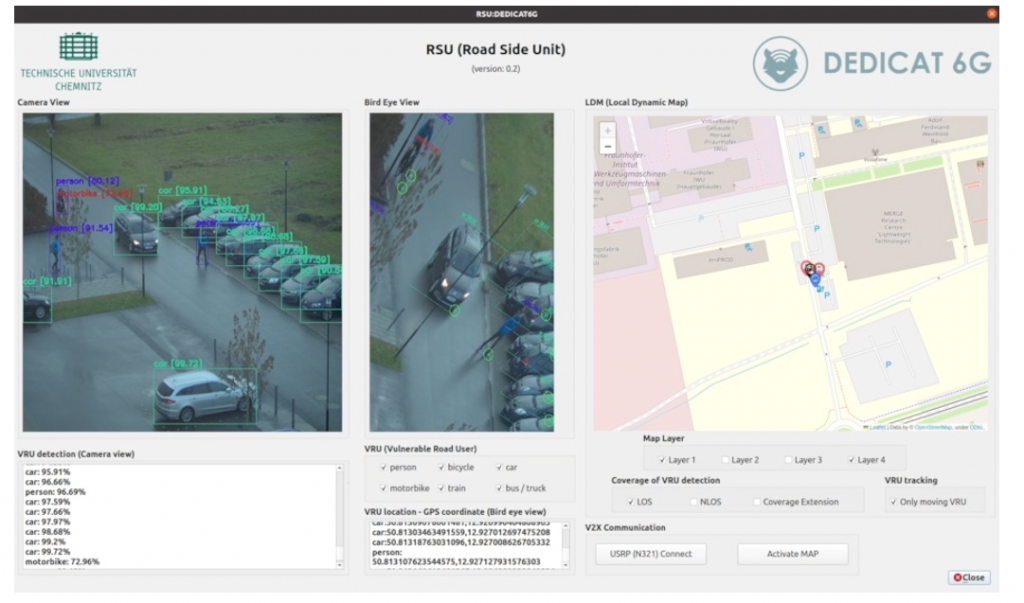
In scenario 1 that is referent to the story 1, we provide a human centric application which has the objective to generate dynamically a Local Dynamic Map of the exit of a highway located in Wommelgem, Belgium. This LDM application will have a server-side and a client-side component. In the server-side, the LDM application will process all the sensor data gathered by the Smart Cars and the VRUs and provide as output a single LDM to all involved users. Moreover, the server-side application will identify potentially dangerous situations and trigger warning messages to the involved clients. In the client-side LDM application, depicted in Figure 77, the map of the specific location of the Smart Highway will show in which the Smart Cars and VRUs will be shown for the connected clients. Moreover, in case of a dangerous situation, a notification will be triggered to the connected users.
The LDM application has the following features:
- VRU and Car detection and location information;
- Notification of obstruction, or warning between road users.
Story 2: Distributed situation knowledge in shared traffic spaces
In scenario 2 that is linked to story 2, the human-centric application basically aims to increase road safety by recognizing VRUs at the road-side and predicting dangerous situations. For this purpose, an RSU application is being developed that runs on NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin device serving as edge computing. A mobile application for pedestrians that can be linked with RSU is also being developed.
The implementation of the RSU application has the following features:
- VRU detection and location information estimation on the road from the camera sensor installed in the RSU;
- Real-time integration of vehicle location received from OBU and VRU location information received from VRU app;
- Update LDM in real time based on integrated VRU information;
- Using the traffic information of LDM to predict situations such as collision risk and send appropriate warning messages to drivers and pedestrians.
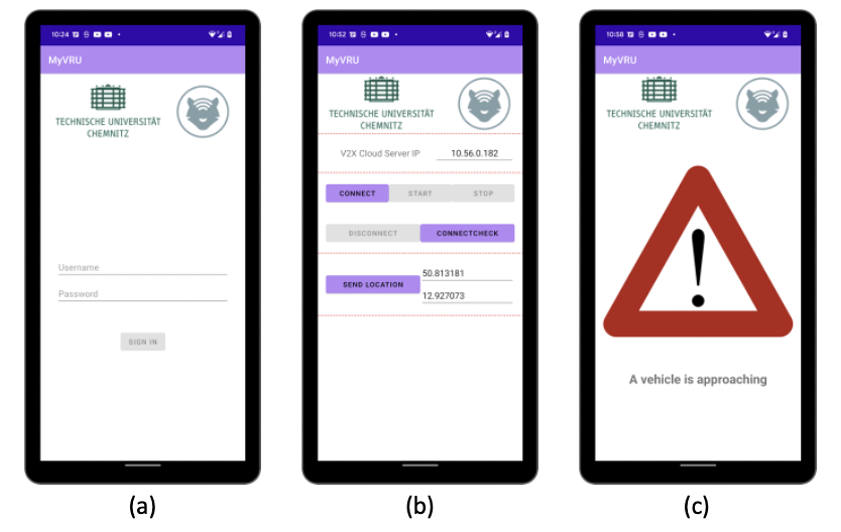
The VRU mobile application based on Android OS, which is compatible with Android 6.0 or higher, has the following features:
- By logging in with a unique ID, RSU recognizes it as a unique VRU user;
- VRU (e.g., pedestrian, cyclist) location can be obtained using the Android smartphone’s onboard GPS transceiver;
- The acquired location information is transmitted to the RSU in real time, including its unique VRU identifier;
- It receives a warning notification from RSU when there is a risk of collision predicted in LDM;
- A warning notification icon and a description of the situation are displayed on the screen.
The Smart Highway pilot will take place in E313 highway, Antwerp, Belgium and B101, Ore Mountains, Germany.